Like hundreds of others, Samantha too loved accessing her smartphone for long hours. Whether it be binge-watching new sitcoms across multiple platforms or impulse shopping, her android was a handy buddy.
One fine day another such shopping impulse lead her to her favorite e-commerce app. However, the already logged in app asked for her credentials multiple times. As soon as she entered her credentials, the details were sent to the hacker. This left her device vulnerable and open to further cyber-attacks that could also lead to several financial losses owing to banking app thefts.
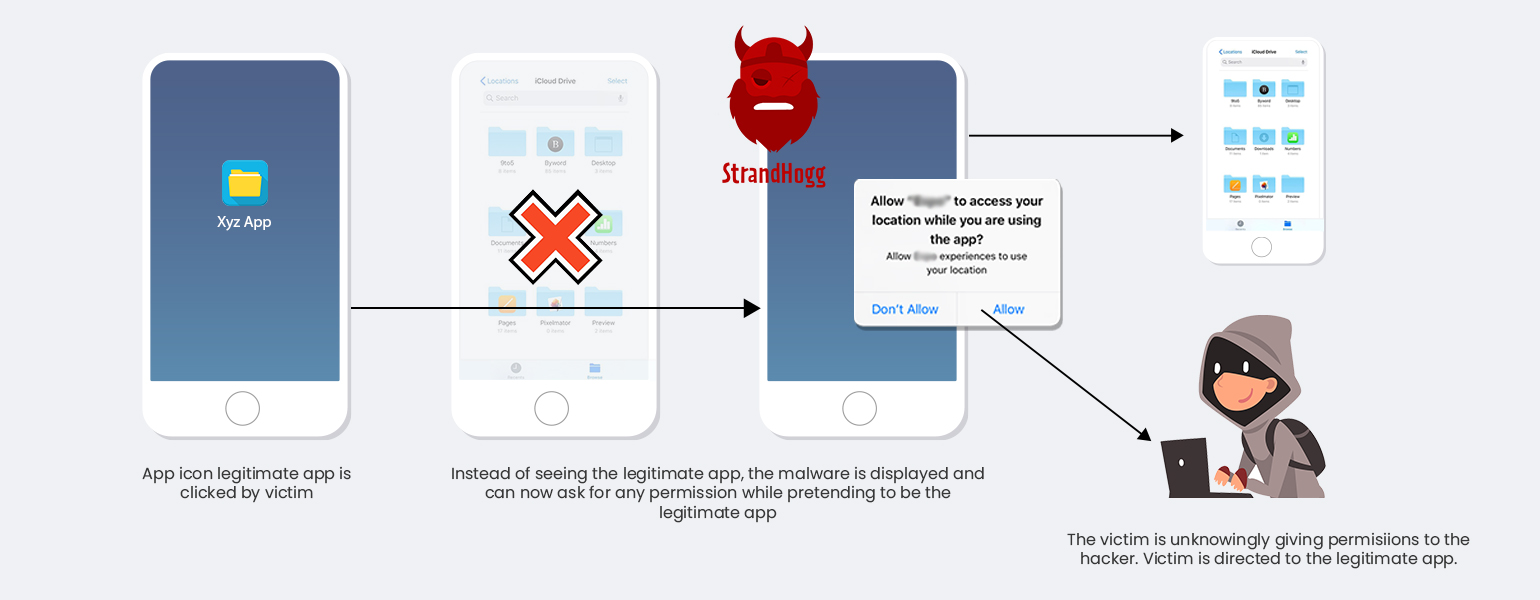
What might simply sound like an imaginary horror story might actually be the case with many of us tomorrow! Ever since an Eastern European security firm noticed a dubious trend of money being siphoned from multiple accounts at a few Czech banks, research was undertaken to identify the snag in security. Further research by Promon led to the identification of StrandHogg. In their research, they state, “Promon security researchers have found proof of a dangerous Android vulnerability, dubbed ‘StrandHogg’, that allows real-life malware to pose as legitimate apps, with users unaware they are being targeted.”
It also deems all of the top 500 most popular apps on Android at risk. Although the Malicious apps reported to Google have been removed, but the researchers at Promon warn that the bug still exists and thus makes every android device vulnerable. The research also concludes that as of now even the devices operating on Android 10 are prone to this vulnerability.
How It Comes Into Play
StrandHogg exists in the Android OS owing to its multitasking capability. The Android’s control setting, taskAffinity, lets any app take on any identity in the multitasking system. This enables any app, even the malicious ones, to request any permission while pretending to be a legitimate app. The attack can be simply in form of seeking permission that seems very natural for the targeted apps. If able to implement this successfully, the attackers can considerably lower the chances of the victims realizing that something is wrong. The users have no idea that they might be granting permission to fake apps.
How to Combat The Threats Owing To This Bug
While proper research is required to find a viable remedy to this issue, our experts at Texala believe that there are a few quicker measures can be paced up as of now, those include:
An effective review mechanism should be put into place that verifies the source code of each and every app before being published on the Google Play Store. Google’s technical team should undertake a detailed analysis of the source code to ensure that no part of it allows any malicious activities. Just as it started blocking the publishing of any new apps which contain the Path traversal Vulnerability, since 2018.
New policy should not allow publishing an android app if:
It affects the user’s system in unexpected ways and/or tries to access the data which it is not authorized to access.
Uses tricks to make the user install the app or contain another app piggybacked on it.
It accesses and transmits the user’s personal data without the user’s consent/knowledge.
Secondly, the teams should also verify whether or not the structure followed to develop code is standard and is not vulnerable to give rise to problems in the future.
Smartphone’s user also need to take care There is no denying that the ratio of apps on Android is way higher than on iOS, however, a bare minimum set of specifications can be defined by the Android OS owners. This would not only strengthen the structure of the operating system to combat the breaches but also would enable a more secure environment for the future.
Moreover, setting up bare minimum restrictions is important for Android as the manufacturers also have a considerable amount of contribution in stopping these attacks. And until Google takes cognizance to strengthen the structure for combating this possibility of breach, a few things can be undertaken by the user itself.
Precautions To Be Taken At The User End
According to the researcher, at present, there is no effective block or a reliable method of detection against StrandHogg on Android devices. However, a few precautionary steps can be taken into account from the user end, which are as follows:
An app or service that you have already logged into asking for a login
Avoid permission pop-ups that do not contain any app’s name
You are possibly at risk when the buttons and links in the user interface do nothing when clicked on
Avoid using apps that have too many typos and mistakes in the user interface
Hygiene Checks to Be Performed At User-End
Check app permissions before installation and abort the installation if the app asks for an unnecessary privilege.
Not to delay installing an update to your OS or an app to prevent any security issue resulting from the exploitation of a recently discovered vulnerability.
If you have some insights about this subject feel free to drop in your message. Our team will be happy to discuss!